1# Assistant
2
3## Assistant Panel
4
5The assistant panel provides you with a way to interact with large language models. The assistant is useful for various tasks, such as generating code, asking questions about existing code, and even writing plaintext, such as emails and documentation. To open the assistant panel, toggle the right dock by using the `workspace: toggle right dock` action in the command palette or by using the `cmd-r` (Mac) or `ctrl-alt-b` (Linux) shortcut.
6
7> **Note**: A custom [key binding](./key-bindings.md) can be set to toggle the right dock.
8
9Once you have configured a provider, you can interact with the provider's language models in a context editor.
10
11To create a new context editor, use the menu in the top right of the assistant panel and select the `New Context` option.
12
13In the context editor, select a model from one of the configured providers, type a message in the `You` block, and submit with `cmd-enter` (or `ctrl-enter` on Linux).
14
15## Setup
16
17- [OpenAI API Setup Instructions](#openai)
18- [OpenAI API Custom Endpoint](#openai-custom-endpoint)
19- [Ollama Setup Instructions](#ollama)
20- [Anthropic API Setup Instructions](#anthropic)
21- [Google Gemini API Setup Instructions](#google-gemini)
22- [GitHub Copilot Chat](#github-copilot)
23
24### Having a Conversation
25
26The assistant editor in Zed functions similarly to any other editor. You can use custom key bindings and work with multiple cursors, allowing for seamless transitions between coding and engaging in discussions with the language models. However, the assistant editor differs with the inclusion of message blocks. These blocks serve as containers for text that correspond to different roles within the conversation. These roles include:
27
28- `You`
29- `Assistant`
30- `System`
31
32To begin, select a model and type a message in a `You` block.
33
34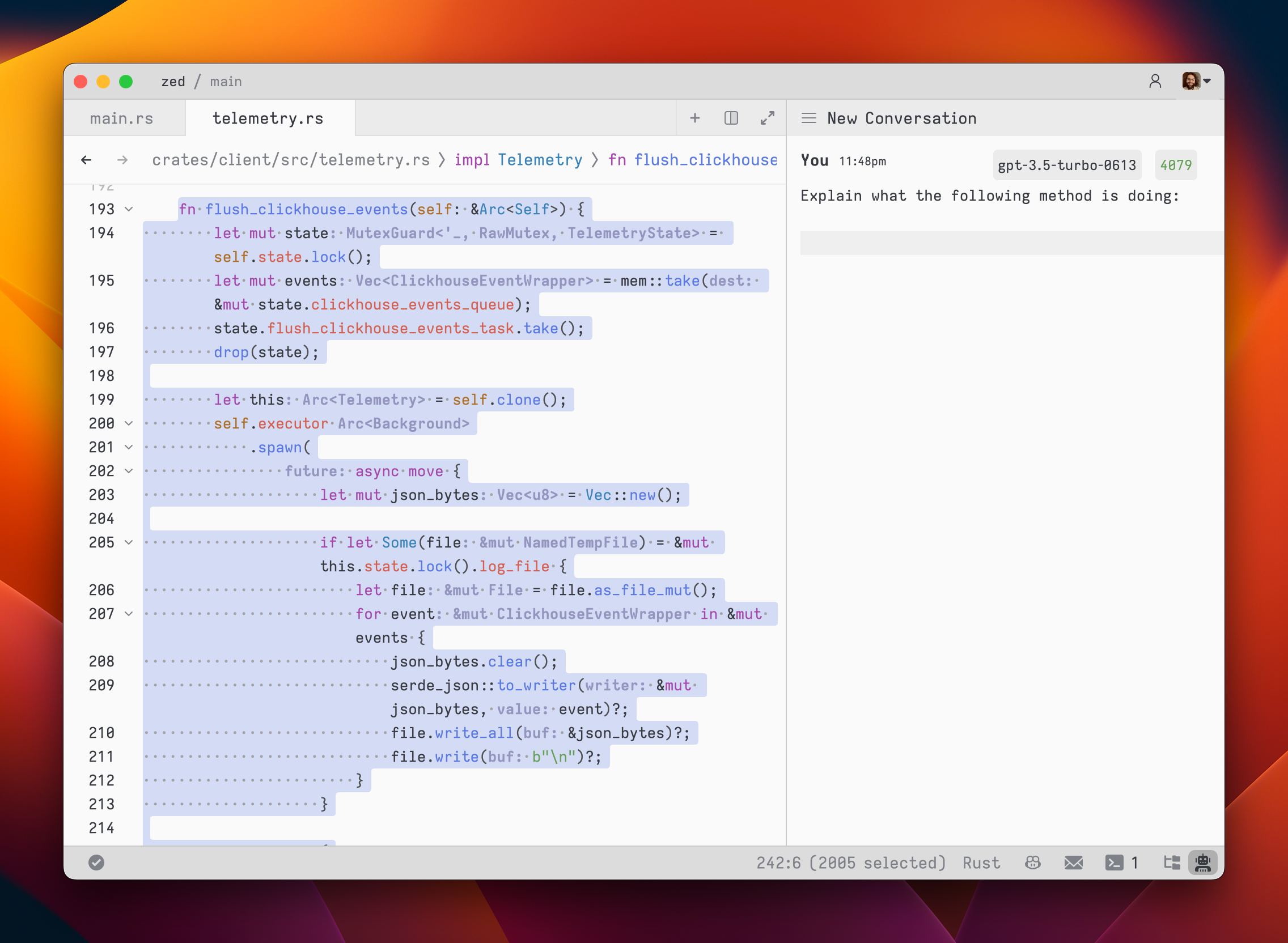
35
36As you type, the remaining tokens count for the selected model is updated.
37
38Inserting text from an editor is as simple as highlighting the text and running `cmd->` (`assistant: quote selection`); Zed will wrap it in a fenced code block if it is code.
39
40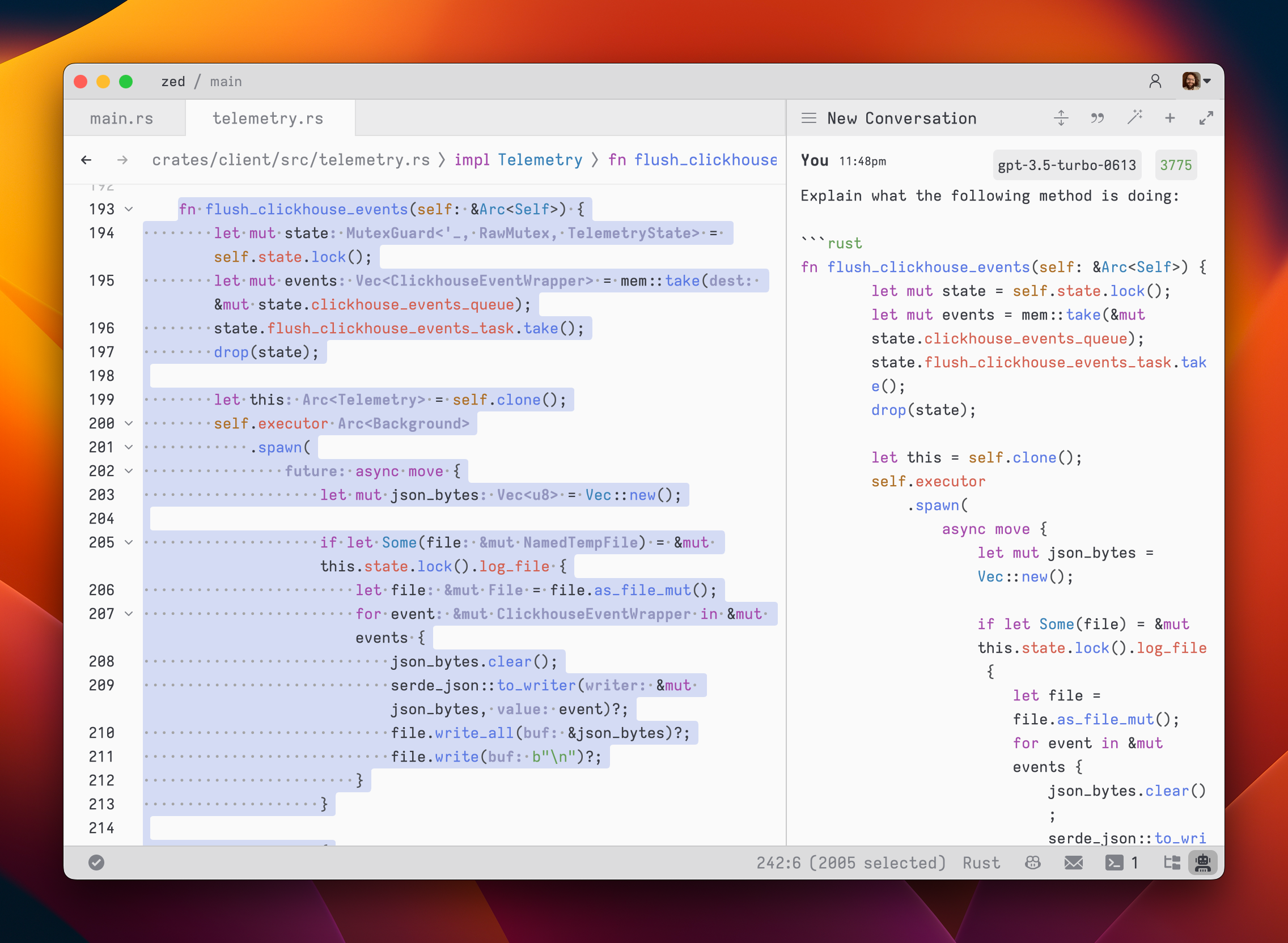
41
42To submit a message, use `cmd-enter` (`assistant: assist`). Unlike typical chat applications where pressing `enter` would submit the message, in the assistant editor, our goal was to make it feel as close to a regular editor as possible. So, pressing `enter` simply inserts a new line.
43
44After submitting a message, the assistant's response will be streamed below, in an `Assistant` message block.
45
46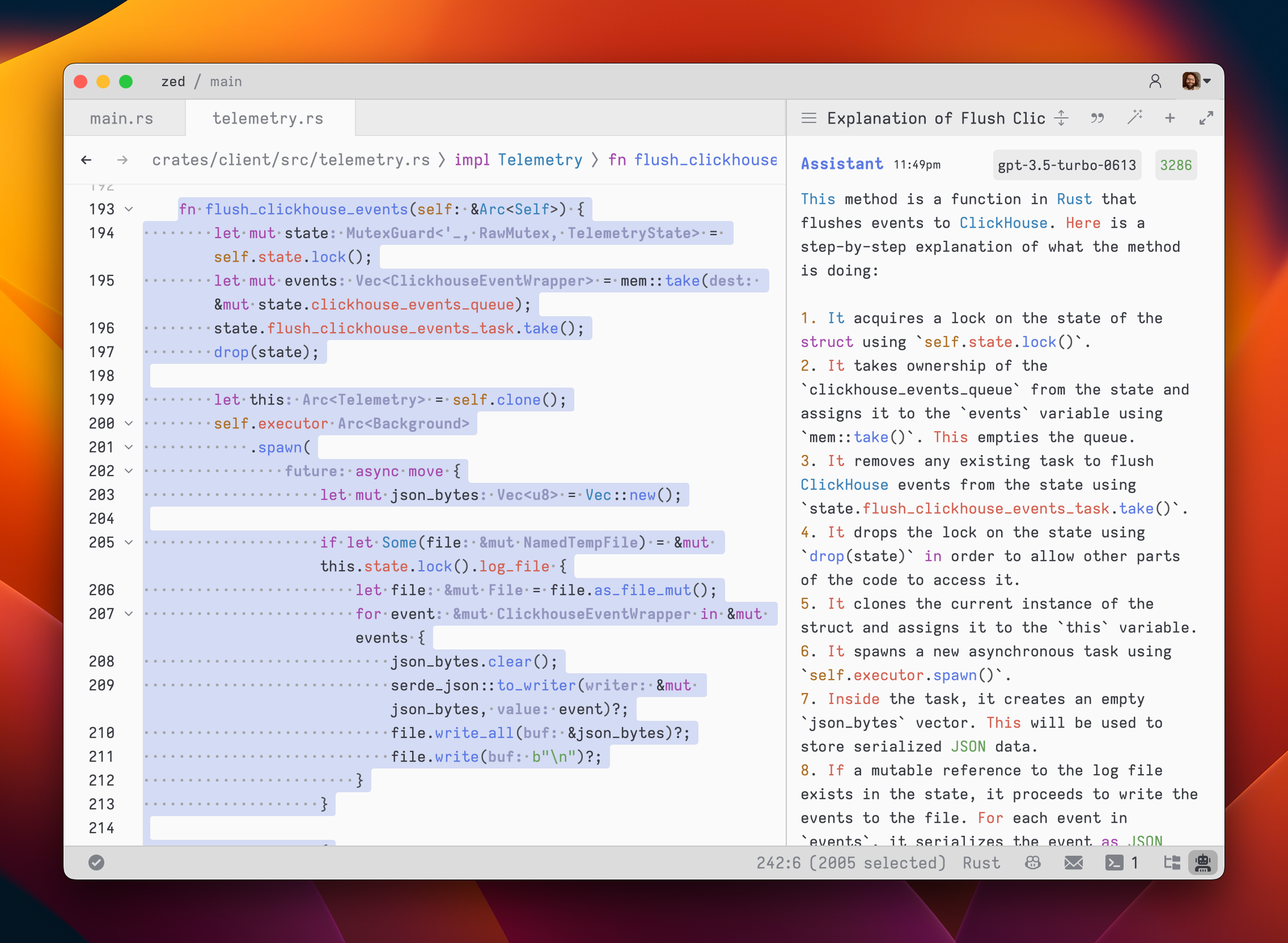
47
48The stream can be canceled at any point with `escape`. This is useful if you realize early on that the response is not what you were looking for.
49
50If you want to start a new conversation at any time, you can hit `cmd-n` or use the `New Context` menu option in the hamburger menu at the top left of the panel.
51
52Simple back-and-forth conversations work well with the assistant. However, there may come a time when you want to modify the previous text in the conversation and steer it in a different direction.
53
54### Editing a Conversation
55
56The assistant gives you the flexibility to have control over the conversation. You can freely edit any previous text, including the responses from the assistant. If you want to remove a message block entirely, simply place your cursor at the beginning of the block and use the `delete` key. A typical workflow might involve making edits and adjustments throughout the conversation to refine your inquiry or provide additional context. Here's an example:
57
581. Write text in a `You` block.
592. Submit the message with `cmd-enter`.
603. Receive an `Assistant` response that doesn't meet your expectations.
614. Cancel the response with `escape`.
625. Erase the content of the `Assistant` message block and remove the block entirely.
636. Add additional context to your original message.
647. Submit the message with `cmd-enter`.
65
66Being able to edit previous messages gives you control over how tokens are used. You don't need to start up a new context to correct a mistake or to add additional context, and you don't have to waste tokens by submitting follow-up corrections.
67
68Some additional points to keep in mind:
69
70- You are free to change the model type at any point in the conversation.
71- You can cycle the role of a message block by clicking on the role, which is useful when you receive a response in an `Assistant` block that you want to edit and send back up as a `You` block.
72
73### Saving and Loading Conversations
74
75After you submit your first message, a name for your conversation is generated by the language model, and the conversation is automatically saved to your file system in `~/.config/zed/conversations`. You can access and load previous messages by clicking on the hamburger button in the top-left corner of the assistant panel.
76
77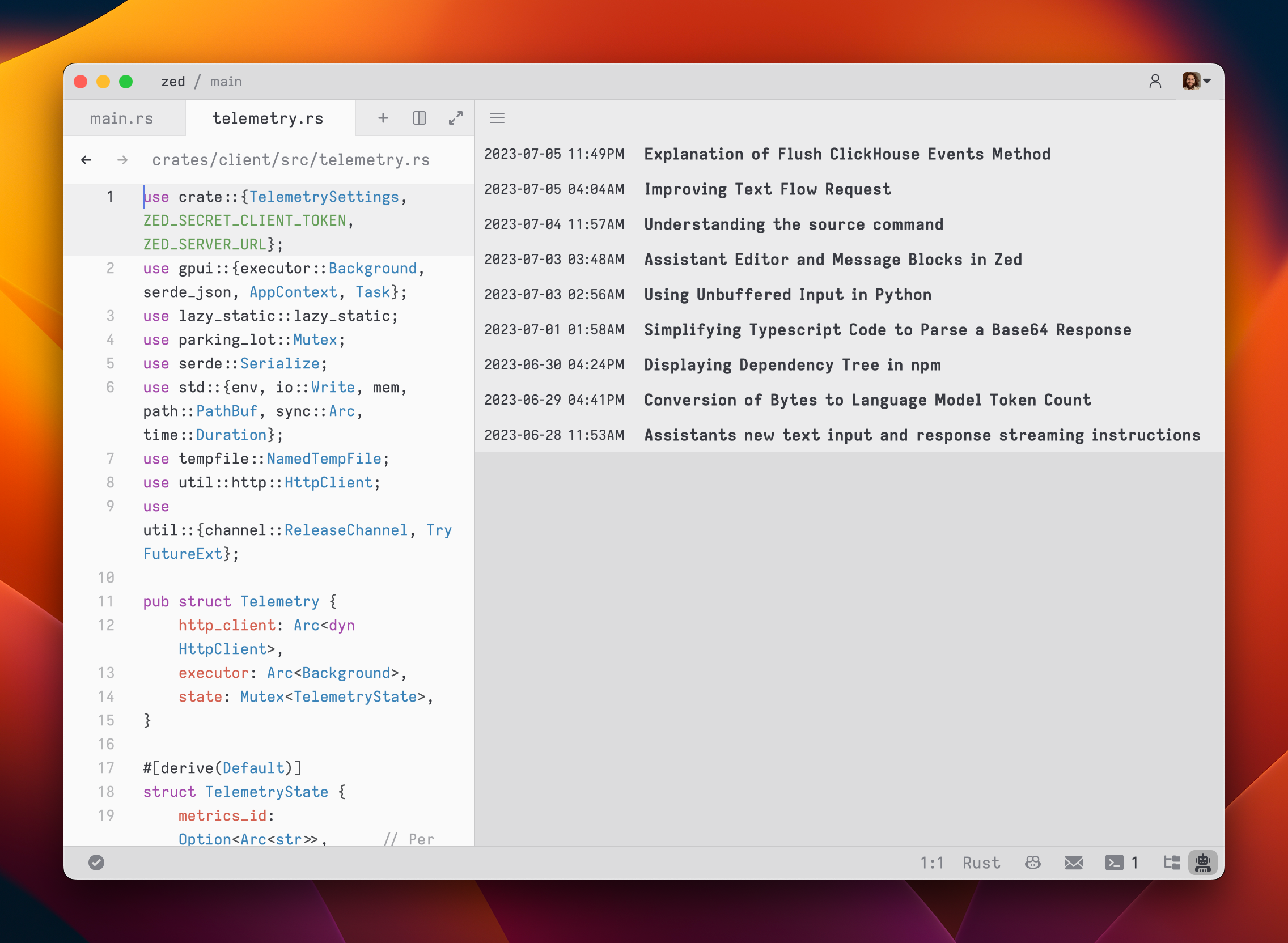
78
79### Adding Prompts
80
81You can customize the default prompts used in new context editors by opening the `Prompt Library`.
82
83Open the `Prompt Library` using either the menu in the top right of the assistant panel and choosing the `Prompt Library` option, or by using the `assistant: deploy prompt library` command when the assistant panel is focused.
84
85### Viewing Past Contexts
86
87You can view all previous contexts by opening the `History` tab in the assistant panel.
88
89Open the `History` using the menu in the top right of the assistant panel and choosing `History`.
90
91### Slash Commands
92
93Slash commands enhance the assistant's capabilities. Begin by typing a `/` at the beginning of the line to see a list of available commands:
94
95- `/default`: Inserts the default prompt into the context
96- `/diagnostics`: Injects errors reported by the project's language server into the context
97- `/fetch`: Inserts the content of a webpage and inserts it into the context
98- `/file`: Inserts a single file or a directory of files into the context
99- `/now`: Inserts the current date and time into the context
100- `/prompt`: Adds a custom-configured prompt to the context (see Prompt Library)
101- `/search`: Performs semantic search for content in your project based on natural language
102- `/symbols`: Inserts the current tab's active symbols into the context
103- `/tab`: Inserts the content of the active tab or all open tabs into the context
104- `/terminal`: Inserts a select number of lines of output from the terminal
105
106## Inline Assistant
107
108You can use `ctrl-enter` to open the inline assistant in both a normal editor, within the assistant panel, and even within the terminal panel.
109
110The inline assistant allows you to send the current selection (or the current line) to a language model and modify the selection with the language model's response. You can also perform multiple generation requests in parallel by pressing `ctrl-enter` with multiple cursors, or by pressing `ctrl-enter` with a selection that spans multiple excerpts in a multibuffer.
111
112The inline assistant pulls its context from the assistant panel, allowing you to provide additional instructions or rules for code transformations.
113
114To create a custom keybinding that prefills a prompt, you can add the following format in your keymap:
115
116```json
117[
118 {
119 "context": "Editor && mode == full",
120 "bindings": {
121 "ctrl-shift-enter": [
122 "assistant::InlineAssist",
123 { "prompt": "Build a snake game" }
124 ]
125 }
126 }
127]
128```
129
130## Advanced: Overriding Prompt Templates
131
132Zed allows you to override the default prompts used for various assistant features by placing custom Handlebars (.hbs) templates in your `~/.config/zed/prompts/templates` directory. The following templates can be overridden:
133
1341. `content_prompt.hbs`: Used for generating content in the editor.
135 Format:
136
137 ```handlebars
138 You are an AI programming assistant. Your task is to
139 {{#if is_insert}}insert{{else}}rewrite{{/if}}
140 {{content_type}}{{#if language_name}} in {{language_name}}{{/if}}
141 based on the following context and user request. Context:
142 {{#if is_truncated}}
143 [Content truncated...]
144 {{/if}}
145 {{document_content}}
146 {{#if is_truncated}}
147 [Content truncated...]
148 {{/if}}
149
150 User request:
151 {{user_prompt}}
152
153 {{#if rewrite_section}}
154 Please rewrite the section enclosed in
155 <rewrite_this></rewrite_this>
156 tags.
157 {{else}}
158 Please insert your response at the
159 <insert_here></insert_here>
160 tag.
161 {{/if}}
162
163 Provide only the
164 {{content_type}}
165 content in your response, without any additional explanation.
166 ```
167
1682. `terminal_assistant_prompt.hbs`: Used for the terminal assistant feature.
169 Format:
170
171 ```handlebars
172 You are an AI assistant for a terminal emulator. Provide helpful responses to
173 user queries about terminal commands, file systems, and general computer
174 usage. System information: - Operating System:
175 {{os}}
176 - Architecture:
177 {{arch}}
178 {{#if shell}}
179 - Shell:
180 {{shell}}
181 {{/if}}
182 {{#if working_directory}}
183 - Current Working Directory:
184 {{working_directory}}
185 {{/if}}
186
187 Latest terminal output:
188 {{#each latest_output}}
189 {{this}}
190 {{/each}}
191
192 User query:
193 {{user_prompt}}
194
195 Provide a clear and concise response to the user's query, considering the
196 given system information and latest terminal output if relevant.
197 ```
198
1993. `edit_workflow.hbs`: Used for generating the edit workflow prompt.
200
2014. `step_resolution.hbs`: Used for generating the step resolution prompt.
202
203You can customize these templates to better suit your needs while maintaining the core structure and variables used by Zed. Zed will automatically reload your prompt overrides when they change on disk. Consult Zed's assets/prompts directory for current versions you can play with.
204
205Be sure you want to override these, as you'll miss out on iteration on our built-in features. This should be primarily used when developing Zed.
206
207## Setup Instructions
208
209### OpenAI
210
211<!--
212TBD: OpenAI Setup flow: Review/Correct/Simplify
213-->
214
2151. Create an [OpenAI API key](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys)
2162. Make sure that your OpenAI account has credits
2173. Open the assistant panel, using either the `assistant: toggle focus` or the `workspace: toggle right dock` action in the command palette (`cmd-shift-p`).
2184. Make sure the assistant panel is focused:
219
220 
221
222The OpenAI API key will be saved in your keychain.
223
224Zed will also use the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable if it's defined.
225
226#### OpenAI Custom Endpoint
227
228You can use a custom API endpoint for OpenAI, as long as it's compatible with the OpenAI API structure.
229
230To do so, add the following to your Zed `settings.json`:
231
232```json
233{
234 "language_models": {
235 "openai": {
236 "api_url": "http://localhost:11434/v1"
237 }
238 }
239}
240```
241
242The custom URL here is `http://localhost:11434/v1`.
243
244### Ollama
245
246Download and install Ollama from [ollama.com/download](https://ollama.com/download) (Linux or macOS) and ensure it's running with `ollama --version`.
247
248You can use Ollama with the Zed assistant by making Ollama appear as an OpenAPI endpoint.
249
2501. Download, for example, the `mistral` model with Ollama:
251
252 ```sh
253 ollama pull mistral
254 ```
255
2562. Make sure that the Ollama server is running. You can start it either via running the Ollama app, or launching:
257
258 ```sh
259 ollama serve
260 ```
261
2623. In the assistant panel, select one of the Ollama models using the model dropdown.
2634. (Optional) If you want to change the default URL that is used to access the Ollama server, you can do so by adding the following settings:
264
265```json
266{
267 "language_models": {
268 "ollama": {
269 "api_url": "http://localhost:11434"
270 }
271 }
272}
273```
274
275### Anthropic
276
277You can use Claude 3.5 Sonnet with the Zed assistant by choosing it via the model dropdown in the assistant panel.
278
279You can obtain an API key [here](https://console.anthropic.com/settings/keys).
280
281Even if you pay for Claude Pro, you will still have to [pay for additional credits](https://console.anthropic.com/settings/plans) to use it via the API.
282
283### Google Gemini
284
285You can use Gemini 1.5 Pro/Flash with the Zed assistant by choosing it via the model dropdown in the assistant panel.
286
287You can obtain an API key [here](https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey).
288
289### GitHub Copilot Chat
290
291You can use GitHub Copilot chat with the Zed assistant by choosing it via the model dropdown in the assistant panel.